The information security industry has long operated with the premise of two, very different kinds of threats: indiscriminate, cyber criminal activity aimed at making money quick and sophisticated, targeted attacks intended to provide long term competitive advantage to another company (or economy), disrupt the operation of the target or provide a (future) strategic advantage in some kind of cyber conflict. But new research from FireEye suggests that the lines between sophisticated and unsophisticated cyber operations are blurred, making it hard for organizations to know if a given infection is merely bad luck, or evidence of a larger and more dangerous operation. Writing about a new financially motivated hacking crew called Fin6, FireEye said that the group, which targeted point-of-sale systems made off with “millions of payment card numbers.” Still, FireEye said that it couldn’t figure out how the group compromised its victims. “In Mandiant’s investigations of FIN6, the group already […]
Fireeye
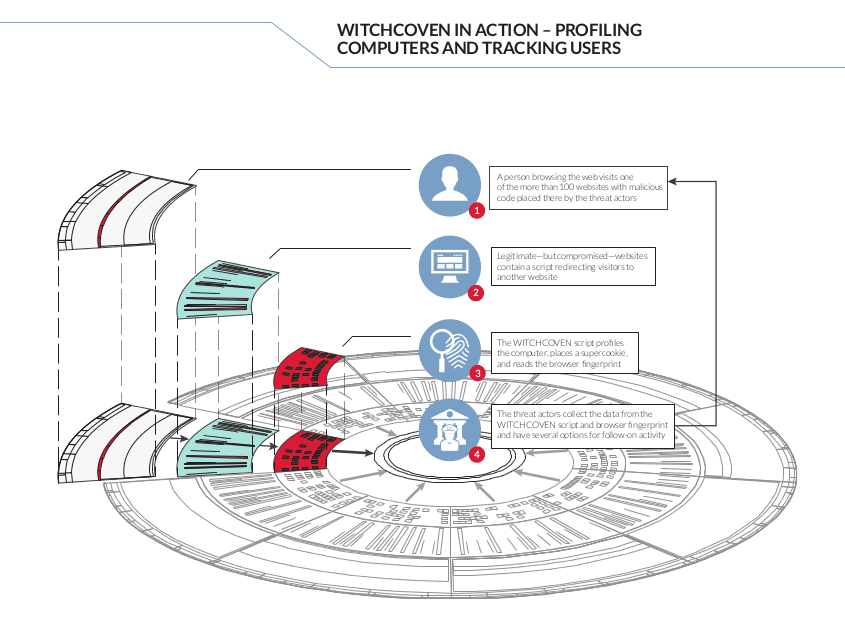
Super Cookies, Web Analytics Behind Malicious Profiling
In-brief: FireEye is warning about a sophisticated campaign of online surveillance that combines web “super cookies” and common analytics software to target individuals with links to international diplomacy, the Russian government and the energy sector.
Report: Cyber Ring Stole Data To Game Stock Market | Reuters
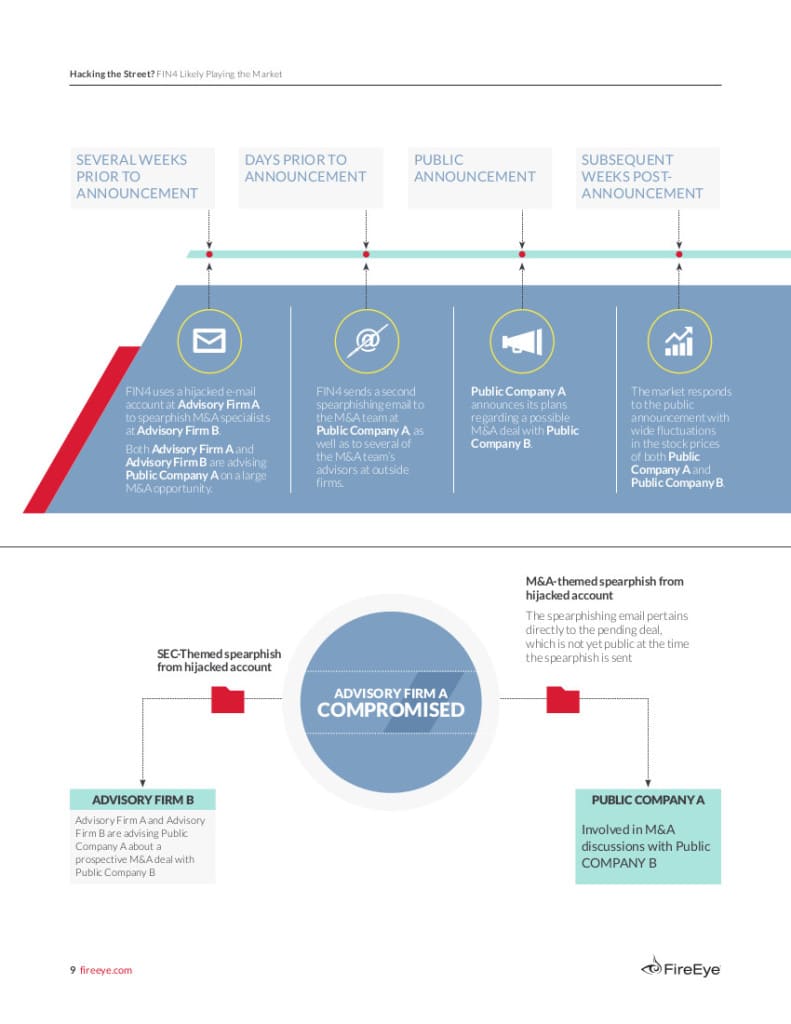
Reuters has the story this morning about a new report out from the folks at FireEye about a cyber espionage ring that targets financial services firms. The campaign, dubbed FIN4 by FireEye, stole corporate secrets for the purpose of gaming the stock market. FireEye believes that the extensive cyber operation compromised sensitive data about dozens of publicly held companies. According to FireEye the victims include financial services firms and those in related sectors, including investment bankers, attorneys and investor relations firms. Rather than attempting to break into networks overtly, the attackers targeted employees within each organization. Phishing e-mail messages led victims to bogus web sites controlled by the hackers, who harvested login credentials to e-mail and social media accounts. Those accounts were then used to expand the hackers reach within the target organization: sending phishing email messages to other employees. The criminals behind FIN4 sought data that could be useful to stock traders, including Securities and […]
Uncle Sam Taking a Back Seat in Cyber Defense | Bloomberg
Bloomberg has a story on the collaborative, private sector effort to thwart an industrial hacking campaign linked to Chinese intelligence. The effort, which involved firms like FireEye and iSight Partners “demonstrates for the first time a private-sector model that they believe can move faster than investigations by law enforcement agencies,” the report said. From the article: The take-down largely bypassed traditional law enforcement tools, relying instead on cooperation between companies that are normally fierce competitors. Coalition members — which include Microsoft Corp., Cisco Inc. and Symantec Corp. — say they can act faster than governments because they operate global Internet systems and have business relationships with tens of thousands of companies. Read more via China-Linked Hacking Foiled by Private-Sector Sleuthing – Businessweek.
Dusting For Malware’s Bloody Prints
Malicious software is nothing new. Computer viruses and worms have been around for decades, as have most other families of malware like remote access tools (RATs) and key loggers. But all our experience with malware hasn’t made the job of knowing when our organization has been hit by it any easier. In fact, recent news stories about breaches at Home Depot, Target, Staples and other organizations makes it clear that even sophisticated and wealthy corporations can easily overlook both the initial compromise and endemic malware infections – and at great cost. That may be why phrases like “dwell time” or “time to discovery” seem to pop up again and again in discussions of breach response. There’s no longer any shame in getting “popped.” The shame is in not knowing that it happened. Greg Hoglund says he has a fix for that latter problem. His new company, Outlier Security, isn’t “next generation […]